Rehab Articles

Talk therapy, also called psychotherapy, can be very effective yet this type of treatment is not often used when it comes to treating bipolar disorder. This disorder includes both manic ups and depressive downs, and the most common treatment for this disorder is a drug called lithium. In fact this drug was considered so effective when it was first available on the market that many mental health professionals use it as the first line of treatment. Today talk therapy is used for a wide range of mental disorders and conditions, but it is rarely used with bipolar disorder patients and this can be a big mistake. Too often professionals reach for a prescription pad in order to solve a problem when other methods may be just as effective.
Talk therapy does not have any dangerous side effects that can be a risk with drugs to treat bipolar disorder, and mental health professionals are starting to change their views on using this therapy. University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine in Pennsylvania associate professor of psychiatry Holly A. Swartz, M.D explained this change in the journal called Focus. Swartz said “Toward the end of the 20th century, it became increasingly apparent that medication offered only partial relief from bipolar disorder. Treatment with pharmacologic interventions alone was associated with disappointingly low rates of remission, high rates of recurrence, residual symptoms, and psychosocial impairment.. Gradually, the field moved from conceptualizing bipolar disorder as a disorder requiring only medication to an illness that, like many chronic disorders, is best treated using a combination of pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy.” Do you think talk therapy should be used before drugs are prescribed? Why or why not?
Rehab Articles
Antipsychotic drugs are commonly prescribed for those who have been diagnosed with schizophrenia, but recent research shows that these drugs can cause brain structure changes when they are used for a long term period. University of Brescia in Italy psychiatry professor and Spedali Civili Hospital psychiatric unit director Dr. Antonio Vita discussed the new research and stated “The role played by antipsychotic treatment on the pathophysiologic trajectory of brain abnormalities in schizophrenia is currently a matter of lively debate.” The study showed that more gray matter in the brain was lost when patients were placed on first generation antipsychotic drugs than what was lost when second generation drugs in this category were used. First generation drugs work differently in the body than second generation drugs in this class do, and that is a possible reason for the difference in gray matter volume and loss.
Dr. Vita treats patients with schizophrenia, and he has seen the imaging results which show the brain structure changes when antipsychotic drugs are used on a long term basis. Vita explained the new research by saying “Although this is a clinically meaningful result, many issues remain to be clarified. For instance, we still do not know whether the effects on the brain of antipsychotics vary as a function of age and stage of illness, or whether they may occur only when a certain threshold of exposure — daily dose or cumulative dose — is reached.. Clarification of these issues will have crucial importance in the clinical management of schizophrenia and will allow a better understanding of the mechanisms underlying the progression of structural brain abnormalities in the disease.” Have you or someone you know ever used these drugs?
Rehab Articles

A number of research studies have shown that probiotics are an important food group that can offer mental health benefits. The study results have shown that individuals who have more good bacteria in their intestines and digestive system tend to have better mental as well as physical health, but why? How does bacteria in your gut affect your mental health? Which foods have probiotics in them? What about supplements? All of these are questions that you probably need answered. More beneficial bacteria in your digestive system promotes faster and more effective detoxification, a stronger immune system, and other positive benefits. People who include more probiotics in their diet generally have fewer negative thoughts, they are less anxious, and they have a better mood than individuals who do not regularly eat fermented foods which naturally contain large numbers of probiotics.
In the studies on probiotics and mental health researchers found that people who did not consume these beneficial bacteria as part of their regular diet had lower levels of brain activity in areas of the brain associated with emotion as well as other functions. An increase in foods with probiotics increased the activity in these brain areas. Foods that are rich in probiotics are usually foods which have been fermented. Yogurt, kombucha, kimchi, and sauerkraut are all foods that have a lot of probiotics in them. When purchasing yogurt make sure that the product actually has live probiotic cultures in order to get the benefits of these good bacteria, some commercial yogurts may have little if any live bacteria cultures.
Rehab Articles
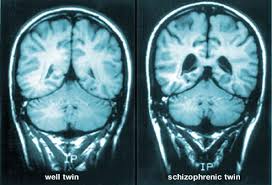
When it comes to schizophrenia early intervention is very important. This step can help improve the quality of life for the patient, reduce the need for extensive and costly hospitalization due to this mental disorder, and improve the treatment outcome. With all of these benefits there is a shortage of early intervention programs and efforts that can make a difference. As soon as someone with schizophrenia starts to show signs that the mental disorder is worsening intervention should occur to prevent the symptoms from becoming worse. As this disorder progresses the individual may lose touch with reality, and it is common for hallucinations and delusions to occur when the disease worsens. These symptoms may put the patient at risk of harming themselves or others, leading to the need for hospitalization.
Early intervention when the first symptoms of schizophrenia start to show can make the difference between a hospital stay that could last for weeks or even months and the ability to stay out of the hospital and lead a better and more productive life. According to National Alliance on Mental Illness medical director and psychiatrist Ken Duckworth “All we ever saw in the ‘80s was the equivalent of stage 4 schizophrenia. It would be as if you were an oncologist, and all you saw were people with metastatic breast cancer.” Until now the focus has been on treating patients after symptoms worsen, but hopefully this will change and more public funding and support will be provided for early intervention programs as well. Do you know someone with schizophrenia who needs help?
Rehab Articles

Bariatric surgery is a surgical procedure used for people who are extremely overweight, and this surgery reduces the stomach size so that the patient consumes fewer calories each day. A new study on adults who have had this procedure shows that the risk of self harm after the surgery may be higher than what is seen in the general population. Bariatric surgery has shown a number of benefits for individuals who are morbidly obese, and these patients often suffer from medical complications linked to obesity like diabetes and cardiovascular problems. Losing weight can minimize or even eliminate these health conditions. People who are morbidly obese also tend to suffer from mental illness and mental health problems as well. That places this population at a higher degree of risk for self harm behaviors even before undergoing bariatric surgery.
Until the recent study it was not clear whether bariatric surgery aggravated the risk of self harm in patients though. Researchers compared the rates of self harm for each patient before the bariatric surgery and after the procedure. The results were surprising. Self harm emergencies increased by more than half after the bariatric surgery was performed, with 111 patients experiencing 158 self harm emergencies post surgery. Almost all of these self harm attempts or incidents occurred in patients who already had one or more mental disorders. According to the researchers “Findings from this study advocate a better understanding of these and other theories through future research of potential mechanisms of self-harm in patients undergoing bariatric surgery. Additional clinical implications include active postoperative screening for self-harm risk among patients who have undergone bariatric surgery and are presenting for follow up. Patient and surgery factors could help identify vulnerable patients. Overall, these findings imply that more work is needed to understand why self-harm behaviors increase in the postoperative period and how these risks might be reduced.”